LAST DAY! ⏳ Secure top scores and your uni dream. 💡Only Rp 90,000 for 40 minutes. Offer ends MIDNIGHT!
LAST DAY! ⏳ Secure top scores and your uni dream.
💡Only Rp 90,000/hour TODAY. Offer ends MIDNIGHT!
LAST DAY! ⏳ Secure top scores and your uni dream. 💡Only Rp 90,000 for 40 minutes. Offer ends MIDNIGHT!
LAST DAY! ⏳ Secure top scores and your uni dream.
💡Only Rp 90,000/hour TODAY. Offer ends MIDNIGHT!
Top Universities

Affordable Cost

Work Opportunities

Scholarships Available

Lower or Free Education Cost




Here are some of the reasons why studying in German is a good idea:
Germany is known for its reasonable cost of living. For students, the monthly costs of living typically fall within the range of 700 – 1,000 EUR, which covers accommodation as well.
Typical courses for Bachelor’s or Master’s degrees are reasonably priced, even at private universities. The expenses associated with pursuing an MBA in Germany, an MS in Germany, or any medical or professional degrees can be quite substantial. The university a student chooses can also play a role in their academic journey.
Tuition Fee for International Students:

For international students from countries where a student visa is necessary to study in Germany, it’s crucial to correctly apply for one at the German Embassy or Consulate in your country. The process of applying for a student visa usually includes several steps.
The student visa application process may differ based on your home country and the specific German Embassy or Consulate, so it’s advised to consult the embassy for updated information and requirements.
Cost Student Applicant Visa in German
The student applicant visa costs 75€, similar to a standard student visa. Students with scholarships from German public institutions, like DAAD, may be exempt from visa processing fees. Payment should be made in local currency, and exchange rates may vary. Payment methods may include cash, credit card, or demand draft. If an application is denied, a refund is not possible.
You can study in Germany with two different sorts of visas, as we’ve already established:
There are several study levels and degree levels for which the national German study visa is available. Undergraduate, graduate, postgraduate, and exchange programs are all included in this. This includes taking part in a non-academic German language course or a pre-academic measure.
You can apply for any one of three categories of German national visas (D visas), depending on your specific situation:
To apply for a student visa to study in German, you’ll need the following:
Note: Your university’s International Office (Akademisches Auslandsamt) can offer the most up-to-date information for both academic and residence-related inquiries.
Students in Germany can obtain health insurance through two main options:
Public Health Insurance
Students under 30 years old, including international students in regular degree programs, can typically enroll in Germany’s public health insurance system. To do this, they can select from several statutory health insurance providers and must provide documents like their university acceptance letter and a valid residence permit.
Private Health Insurance
Some international students might not be eligible for public health insurance or prefer private insurance for specific reasons. Private health insurance is an option for the following:






When it comes to private health insurance, there are various options available at different price points. The most affordable plan can be found starting from EUR 33, with the cost varying based on the specific provider and policy you opt for.
Keep in mind the following steps to obtain health insurance in Germany as an international student:

• Lancaster University Leipzign
• European Universityn
• GISMA Business School
• International University of Applied Sciences (IU)
• Jacobs University International College (JUIC)
• GISMA Business School
• Lancaster University Leipzig
• Jacobs University International College (JUIC)
• International University of Applied Sciences (IU)
• Lancaster University Leipzig
• GISMA Business School
• International University of Applied Sciences (IU)

• International University of Applied Sciences (IU)
• GISMA Business School
• Jacobs University International College (JUIC)
| Accommodation expenses in German for international students | Expenses (approx) |
|---|---|
| Student Halls of Residence (Studentenwohnheim) | 180 to 332 EUR per month |
| Private Accommodation | 400 to 600 EUR per month |
| Homestay | 379 to 595 EUR per month |









International students are eligible to work part-time if they meet the following regulations:
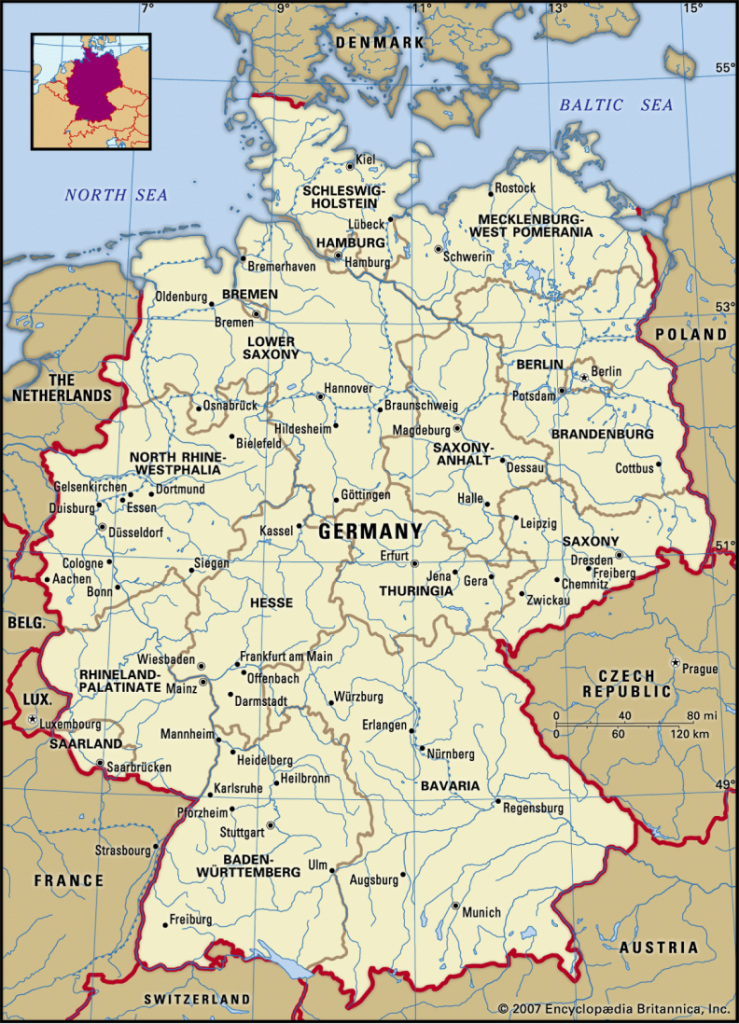
Germany’s central and southern regions boast picturesque forested hills and majestic mountains, which are traversed by the stunning river valleys of the Danube, Main, and Rhine. The landscape in the north transforms into a vast plain that extends all the way to the North Sea. Germany is a country that offers an incredible range of experiences. Germany’s strategic position in the heart of Europe has greatly influenced its complex and eventful history. It shares borders with nine neighboring countries, which is the highest number among all European countries. The largest wooded area in Germany, located in the southwest near the Swiss border, is widely renowned. Welcome to the Black Forest, a breathtaking mountainous region adorned with majestic pines and fir trees. This forest is home to the source of the Danube, which happens to be one of the longest rivers in Europe.
Germany shares its northern border with Denmark on the Jutland peninsula, and its western borders with The Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, France, Switzerland, Austria, and the Czech Republic. The country’s easternmost border connects with Poland, symbolizing the transfer of Germany’s eastern territories to Poland. Germany’s physical geography features are diverse, encompassing vast east-west morphological zones typical of central Europe. The southern part of Germany borders the outermost ranges of the Alps, while the central German uplands form a crucial part of a broader European expanse. Germany’s landscape features forested block mountains, intermediate plateaus with steep edges, and lowland basins. The North German Plain, also known as the Lowland, is part of the larger North European Plain, extending from the Low Countries in the west to Germany, Poland, Belarus, the Baltic states, and Russia in the east. The country’s topography varies from towering peaks of the Bavarian Alps to lower-lying areas near the coast. The surface configuration of Germany’s landscape is shaped by erosion, valleys, valley glaciers, and weathered material. The Alpine Foreland is a result of the Alpine orogeny and volcanic activity.
Do’s
Don’ts

Top Universities

Affordable Cost

Work Opportunities

Scholarships Available

Lower or Free Education Cost




Here are some of the reasons why studying in German is a good idea:
Germany is known for its reasonable cost of living. For students, the monthly costs of living typically fall within the range of 700 – 1,000 EUR, which covers accommodation as well.
Typical courses for Bachelor’s or Master’s degrees are reasonably priced, even at private universities. The expenses associated with pursuing an MBA in Germany, an MS in Germany, or any medical or professional degrees can be quite substantial. The university a student chooses can also play a role in their academic journey.
Tuition Fee for International Students:

For international students from countries where a student visa is necessary to study in Germany, it’s crucial to correctly apply for one at the German Embassy or Consulate in your country. The process of applying for a student visa usually includes several steps.
The student visa application process may differ based on your home country and the specific German Embassy or Consulate, so it’s advised to consult the embassy for updated information and requirements.
Cost Student Applicant Visa in German
The student applicant visa costs 75€, similar to a standard student visa. Students with scholarships from German public institutions, like DAAD, may be exempt from visa processing fees. Payment should be made in local currency, and exchange rates may vary. Payment methods may include cash, credit card, or demand draft. If an application is denied, a refund is not possible.
You can study in Germany with two different sorts of visas, as we’ve already established:
There are several study levels and degree levels for which the national German study visa is available. Undergraduate, graduate, postgraduate, and exchange programs are all included in this. This includes taking part in a non-academic German language course or a pre-academic measure.
You can apply for any one of three categories of German national visas (D visas), depending on your specific situation:
To apply for a student visa to study in German, you’ll need the following:
Note: Your university’s International Office (Akademisches Auslandsamt) can offer the most up-to-date information for both academic and residence-related inquiries.

• Lancaster University Leipzign
• European Universityn
• GISMA Business School

• International University of Applied Sciences (IU)
• Jacobs University International College (JUIC)
• GISMA Business School

• Lancaster University Leipzig
• Jacobs University International College (JUIC)
• International University of Applied Sciences (IU)

• Lancaster University Leipzig
• GISMA Business School
• International University of Applied Sciences (IU)

• International University of Applied Sciences (IU)
• GISMA Business School
• Jacobs University International College (JUIC)
| Accommodation expenses in German for international students | Expenses (approx) |
|---|---|
| Student Halls of Residence (Studentenwohnheim) | 180 to 332 EUR per month |
| Private Accommodation | 400 to 600 EUR per month |
| Homestay | 379 to 595 EUR per month |

Register With Gold Star Education And Talk With Our Expert Counsellor








International students are eligible to work part-time if they meet the following regulations:

Germany’s central and southern regions boast picturesque forested hills and majestic mountains, which are traversed by the stunning river valleys of the Danube, Main, and Rhine. The landscape in the north transforms into a vast plain that extends all the way to the North Sea. Germany is a country that offers an incredible range of experiences. Germany’s strategic position in the heart of Europe has greatly influenced its complex and eventful history. It shares borders with nine neighboring countries, which is the highest number among all European countries. The largest wooded area in Germany, located in the southwest near the Swiss border, is widely renowned. Welcome to the Black Forest, a breathtaking mountainous region adorned with majestic pines and fir trees. This forest is home to the source of the Danube, which happens to be one of the longest rivers in Europe.
Germany shares its northern border with Denmark on the Jutland peninsula, and its western borders with The Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, France, Switzerland, Austria, and the Czech Republic. The country’s easternmost border connects with Poland, symbolizing the transfer of Germany’s eastern territories to Poland. Germany’s physical geography features are diverse, encompassing vast east-west morphological zones typical of central Europe. The southern part of Germany borders the outermost ranges of the Alps, while the central German uplands form a crucial part of a broader European expanse. Germany’s landscape features forested block mountains, intermediate plateaus with steep edges, and lowland basins. The North German Plain, also known as the Lowland, is part of the larger North European Plain, extending from the Low Countries in the west to Germany, Poland, Belarus, the Baltic states, and Russia in the east. The country’s topography varies from towering peaks of the Bavarian Alps to lower-lying areas near the coast. The surface configuration of Germany’s landscape is shaped by erosion, valleys, valley glaciers, and weathered material. The Alpine Foreland is a result of the Alpine orogeny and volcanic activity.
Do’s
Don’ts
Customer Service
Customer Service

Enhance your platform experience to the fullest.
Register now and unlock a world of exclusive benefits tailored just for you.