LAST DAY! ⏳ Secure top scores and your uni dream. 💡Only Rp 90,000 for 40 minutes. Offer ends MIDNIGHT!
LAST DAY! ⏳ Secure top scores and your uni dream.
💡Only Rp 90,000/hour TODAY. Offer ends MIDNIGHT!
LAST DAY! ⏳ Secure top scores and your uni dream. 💡Only Rp 90,000 for 40 minutes. Offer ends MIDNIGHT!
LAST DAY! ⏳ Secure top scores and your uni dream.
💡Only Rp 90,000/hour TODAY. Offer ends MIDNIGHT!

High-Quality Education

Affordable Cost

Work Opportunities

Safe and Peaceful

Great place to live




Here are some of the reasons why studying in Japan is a good idea:
The average cost of living in Japan is significantly influenced by the price of attending the country’s top institutions, around 876,000 – 1.188,000 JPY. Studying in Japan should cost approximately 817,800 JPY at National Universities and 1,146,819 JPY at Private Liberal Arts Universities. While private science institutions may charge 1,501,233 JPY public universities may charge anything from 931,235 JPY to 1,501,235 JPY. If you’ve been wondering what the minimum cost of living in Japan is, these numbers should give you a rough sense. Together with your rent and other essential expenses, you should also include the cost of your application and national health insurance in this total. Typically, enrollment and application fees range from 280,000 JPY to 390,000 JPY.
Tuition fees vary depending on the discipline you choose to study, the degree level, and the university in which you enroll. Tuition for international students:

The Japanese Student Visa is a long-term visa that is recognised and accepted by various educational institutions in Japan, including universities, schools, and vocational institutions. Obtaining a Japan Student Visa is a requirement for individuals aspiring to pursue their education in a Japanese educational institution.
The Japanese government has implemented a visa exemption policy for citizens of several countries. Nevertheless, the exemption applies solely to short-term activities like tourism, visits, business engagements, or conference attendance. If you happen to be visa-exempt but have plans to stay in Japan for more than 90 days, it is still necessary for you to apply for a visa that aligns with the purpose of your travel.
Student visa Japan requirements
Overview of The Process and Key aspects
To apply for a student visa to study in Japan, you’ll need the following:
National Health Insurance (NHI)
NHI is for everyone else – students, freelancers, people who work for small companies, and a lot of foreigners find themselves signing up for this in the early stages of their visit. Your contribution is based on your yearly income and might cost you a little more than SHI would – although the first year is often very cheap. You have to sign up for it yourself at your local office that’s run by the regional administration.
Social Health Insurance (SHI)
SHI is the public healthcare system for everyone who’s employed full-time by a medium to large company. While a few subtly different types exist depending on the type of job you have, it offers much the same set of benefits across the board. You and your employer contribute equally to SHI, each paying around 5% of your salary.
Nursing Insurance
A further 1.65% of your earnings go towards nursing insurance if you’re aged between 40 and 65.
International Health Insurance
Japanese hospitals don’t tend to accept this themselves, so if you’re covered by an international insurer you might need to pay the hospital yourself and claim money back afterwards. Make sure you know your policy and what it covers you for.
Private health insurance
Because the public system is both compulsory and quite thorough, private health insurance isn’t as all-encompassing as it is in some countries. However, policies are available to supplement public insurance via money towards the 30% of bills you have to pay, and lump sums in the event of serious medical need.


Typically, you will apply for National Health Insurance when you register your resident status at your local city hall or ward office not long after arriving in Japan.
At iCLA, the student support staff will apply for you on your behalf as part of your resident registration process at city hall.

• The University of Tokyo
• Waseda University
• Yamanashi Gakuin University (ICLA)
• The University of Tokyo
• Yamanashi Gakuin University (ICLA)
• Kyoto University

• The University of Tokyo
• Yamanashi Gakuin University (ICLA)
• Chiba University

• University of Tokyo
• Kyoto University
• Yamanashi Gakuin University (ICLA)
• Le Cordon Bleu - Kobe
• Le Cordon Bleu - Tokyo
• Hattori Nutrition College
| Accommodation expenses in Japan for international students | Expenses (approx) |
|---|---|
| University Dormitories | 12,000 JPY per month |
| Private Apartments | 50,000 JPY to 70,000 JPY per month |
| Share Houses | 55,000 JPY to 70,000 JPY per month |
| Homestay Programs | 93,500 JPY to 170,500 JPY per month |









International students with a “student” visa status are typically not allowed to work in Japan, but can work part-time as long as it doesn’t disrupt their studies. They must use their income for supporting their studies and living expenses, and obtain permission from the Japanese Minister of Justice. Potential employers must inform the Employment Service Centre of their intention to hire foreigners. To work in Japan while studying, international students need to adhere to the following guidelines:
Document Required for Work in Japan
International students are eligible to work part-time if they meet the following requirements:
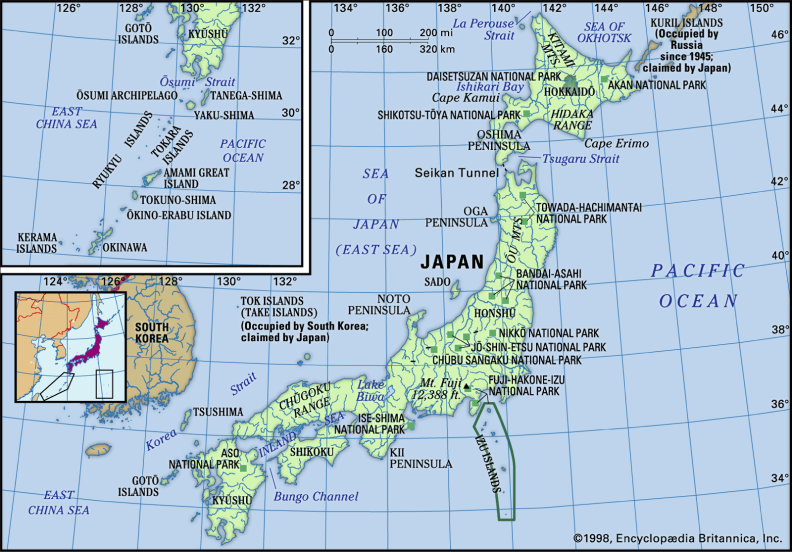
Japan is a captivating archipelago situated on the eastern edge of Asia. Discover the captivating allure of Japan’s four main islands: Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu. In addition, there are nearly 4,000 smaller islands to explore! Japan is strategically located between the Siberian region of Russia in the north and Korea and China farther south, making it an ideal hub for international connections. A significant portion of Japan’s landscape is dominated by majestic mountains. The majestic Japanese Alps stretch across the heart of Honshu, the largest island in Japan. Mount Fuji, the majestic cone-shaped volcano, holds great significance in Japanese culture and is revered by countless individuals. Japan can present certain challenges. Three of the tectonic plates that make up Earth’s crust come together in close proximity and frequently interact, resulting in the occurrence of earthquakes. Japan experiences over a thousand earthquakes annually. Japan boasts an impressive number of approximately 200 volcanoes, with a remarkable 60 of them being active.
Japan is surrounded by various bodies of water, including the Sea of Japan, the Pacific Ocean, the Sea of Okhotsk, and the East China Sea. It shares borders with South and North Korea, Russia, and China. The southern Kuril Islands have been under Soviet and Russian administration since World War II. Tsushima Island is situated between northwestern Kyushu and southeastern South Korea, serving as a natural boundary between the Korea Strait and the Tsushima Strait.
Do’s
Don’ts

High-Quality Education

Affordable Cost

Work Opportunities

Safe and Peaceful

Great place to live




Here are some of the reasons why studying in Japan is a good idea:
The average cost of living in Japan is significantly influenced by the price of attending the country’s top institutions, around 876,000 – 1.188,000 JPY. Studying in Japan should cost approximately 817,800 JPY at National Universities and 1,146,819 JPY at Private Liberal Arts Universities. While private science institutions may charge 1,501,233 JPY public universities may charge anything from 931,235 JPY to 1,501,235 JPY. If you’ve been wondering what the minimum cost of living in Japan is, these numbers should give you a rough sense. Together with your rent and other essential expenses, you should also include the cost of your application and national health insurance in this total. Typically, enrollment and application fees range from 280,000 JPY to 390,000 JPY.
Tuition fees vary depending on the discipline you choose to study, the degree level, and the university in which you enroll. Tuition for international students:

The Japanese Student Visa is a long-term visa that is recognised and accepted by various educational institutions in Japan, including universities, schools, and vocational institutions. Obtaining a Japan Student Visa is a requirement for individuals aspiring to pursue their education in a Japanese educational institution.
The Japanese government has implemented a visa exemption policy for citizens of several countries. Nevertheless, the exemption applies solely to short-term activities like tourism, visits, business engagements, or conference attendance. If you happen to be visa-exempt but have plans to stay in Japan for more than 90 days, it is still necessary for you to apply for a visa that aligns with the purpose of your travel.
Student visa Japan requirements
Overview of The Process and Key aspects
To apply for a student visa to study in Japan, you’ll need the following:

• The University of Tokyo
• Waseda University
• Yamanashi Gakuin University (ICLA)

• The University of Tokyo
• Yamanashi Gakuin University (ICLA)
• Kyoto University

• The University of Tokyo
• Yamanashi Gakuin University (ICLA)
• Chiba University

• University of Tokyo
• Kyoto University
• Yamanashi Gakuin University (ICLA)

• Le Cordon Bleu – Kobe
• Le Cordon Bleu – Tokyo
• Hattori Nutrition College
| Accommodation expenses in Japan for international students | Expenses (approx) |
|---|---|
| University Dormitories | 12,000 JPY per month |
| Private Apartments | 50,000 JPY to 70,000 JPY per month |
| Share Houses | 55,000 JPY to 70,000 JPY per month |
| Homestay Programs | 93,500 JPY to 170,500 JPY per month |

Register With Gold Star Education And Talk With Our Expert Counsellor








International students with a “student” visa status are typically not allowed to work in Japan, but can work part-time as long as it doesn’t disrupt their studies. They must use their income for supporting their studies and living expenses, and obtain permission from the Japanese Minister of Justice. Potential employers must inform the Employment Service Centre of their intention to hire foreigners. To work in Japan while studying, international students need to adhere to the following guidelines:
Document Required for Work in Japan
International students are eligible to work part-time if they meet the following requirements:

Japan is a captivating archipelago situated on the eastern edge of Asia. Discover the captivating allure of Japan’s four main islands: Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu. In addition, there are nearly 4,000 smaller islands to explore! Japan is strategically located between the Siberian region of Russia in the north and Korea and China farther south, making it an ideal hub for international connections. A significant portion of Japan’s landscape is dominated by majestic mountains. The majestic Japanese Alps stretch across the heart of Honshu, the largest island in Japan. Mount Fuji, the majestic cone-shaped volcano, holds great significance in Japanese culture and is revered by countless individuals. Japan can present certain challenges. Three of the tectonic plates that make up Earth’s crust come together in close proximity and frequently interact, resulting in the occurrence of earthquakes. Japan experiences over a thousand earthquakes annually. Japan boasts an impressive number of approximately 200 volcanoes, with a remarkable 60 of them being active.
Japan is surrounded by various bodies of water, including the Sea of Japan, the Pacific Ocean, the Sea of Okhotsk, and the East China Sea. It shares borders with South and North Korea, Russia, and China. The southern Kuril Islands have been under Soviet and Russian administration since World War II. Tsushima Island is situated between northwestern Kyushu and southeastern South Korea, serving as a natural boundary between the Korea Strait and the Tsushima Strait.
Do’s
Don’ts
Customer Service
Customer Service

Enhance your platform experience to the fullest.
Register now and unlock a world of exclusive benefits tailored just for you.